Describe Evidence That the First Prokaryotes Produced Atp by Glycolysis
Krebs Cylce ETC 32-34 total of 36-38. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis.

Pdf Fast Acting Allosteric Phosphofructokinase Inhibitors Block Trypanosome Glycolysis And Cure Acute African Trypanosomiasis In Mice
Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism 21.
. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell and what role the allosteric enzyme phosphofructokinase plays in this process. Up to 24 cash back Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP.
Glycolysis does not require oxygen. Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell and what role the allosteric enzyme phosphofructokinase plays in this process. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis 23.
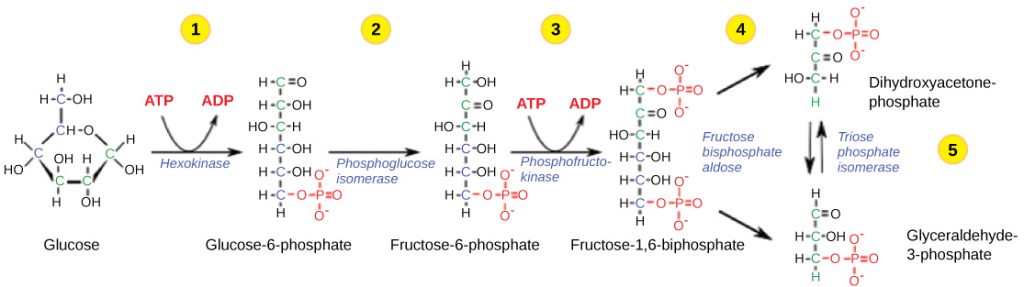
The first step in glycolysis is catalyzed by hexokinase an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. 25 Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. Describe ATP transport and how ATP is used in cells.
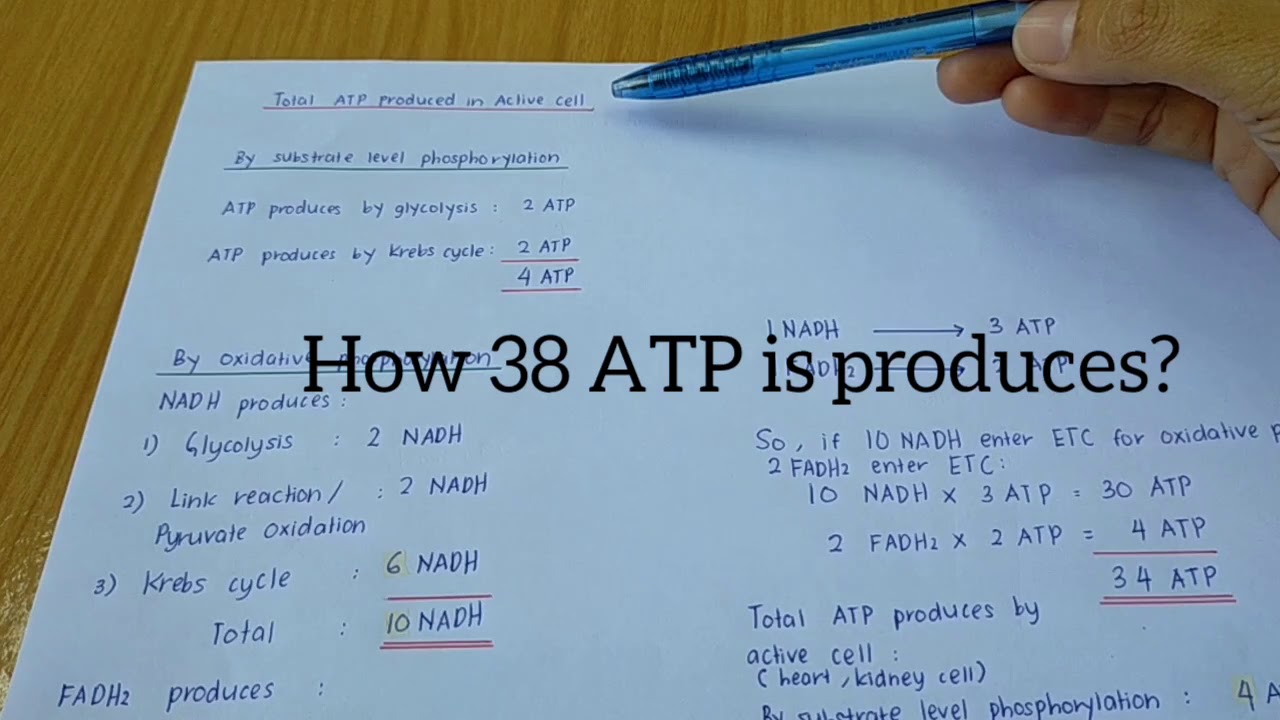
Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. Electron transport begins with several molecules of NADH and FADH2 from the Krebs cycle and transfers their energy into as many as 34 more ATP molecules. The electrons from NADH made in glycolysis are passed to pyruvate restoring the NADrequired to sustain glycolysis.
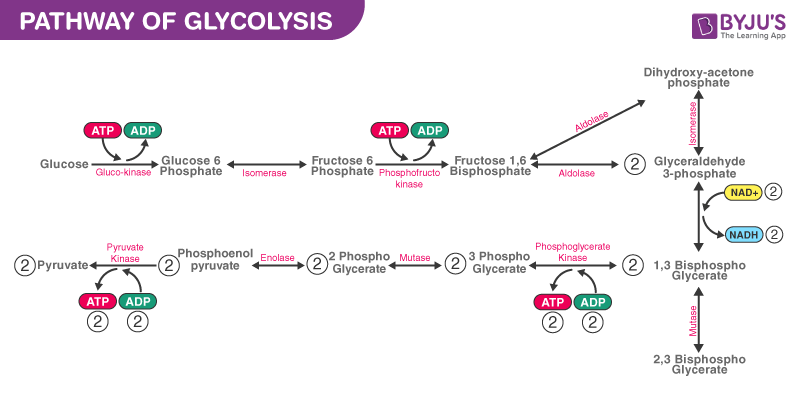
Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell and what role the allosteric. Explain why fermentation is necessary 20. The first half of glycolysis uses two ATP molecules in the phosphorylation of glucose which is then split into two three-carbon molecules.
Explain why fermentation is necessary 20. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis 23. Explain why fermentation is necessary 20.
As ATP is used for energy a phosphate group is detached and ADP is produced. Energy derived from glucose catabolism is used to recharge ADP into ATP. This metabolic process has a connection with the evolution.
Net Gain of 2 in glycolysis 2 ATP. Compare the processes of fermentation and cellular respiration. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP.
Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. 24 Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. Overall the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules for the cell to use for energy.
The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphate groups attached. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell and what role the allosteric enzyme phosphofructokinase plays in this process.
Describe the ways in which ATP can be used to perform cell work. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP 22. How many ATP molecules are produced by glycolysis.
Energy derived from glucose catabolism is used to recharge ADP into ATP. Glycolysis does not require oxygen. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP 22.
Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. Answered by wiki 22112021. Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy.
Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy. The first phase of glycolysis requires energy while the second phase completes the conversion to pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Up to 24 cash back 18.
The first half of glycolysis. Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell and what role the allosteric enzyme phosphofructokinase plays in this process. As ATP is used for energy a phosphate group is detached and ADP is produced.
This process might be linked with the period when oxygen was not present in the atmosphere 35 billion years ago. This means that it can take place in the absence of water. Photosynthesis in Nature Distinguish between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
Explain how glycolysis and the Krebs cycle can contribute to anabolic pathways. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. Prokaryotes date back to time before there were significant amounts of oxygen in atmosphere Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP.
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP molecules and the Krebs cycle produces 2 more. Up to 24 cash back Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the help of oxygen pp. The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphate groups attached.
170-172 FIGURES 917 918 Fermentation is anaerobic catabolism of organic nutrients. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. So the Answer is B.
It yields ATP from glycolysis. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced atp by glycolysis Glycolysis is a process cellular respiration where glucose molecule is broken into pyruvate molecule. Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP 22.
Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. Describe the fate of pyruvate in the absence of oxygen 19. This means that it can take place in the absence of water.
Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. Up to 24 cash back 18.
They were first prokaryotic cells. Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis. The first prokaryotes found at that time are also supposed to produce ATP via glycolysis.
Describe evidence that the first prokaryotes produced ATP by glycolysis 23. Describe the fate of pyruvate in the absence of oxygen 19. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism 21.
26 Explain how ATP production is controlled by the cell and what role the allosteric. Describe the fate of pyruvate in the absence of oxygen 19. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism 21.
Describe how food molecules other than glucose can be oxidized to make ATP. Building protein molecule moving molecules provides muscular movement.

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

Cellular Respiration Biology For Majors I

Glycolysis Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

The Most Common Glycolytic Routes In Prokaryotes Emp Often Simply Download Scientific Diagram

Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation Flashcards Quizlet
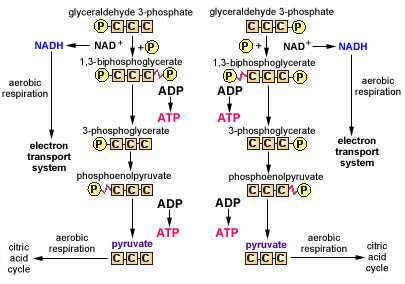
Aerobic Respiration Part 1 Glycolysis Principles Of Biology
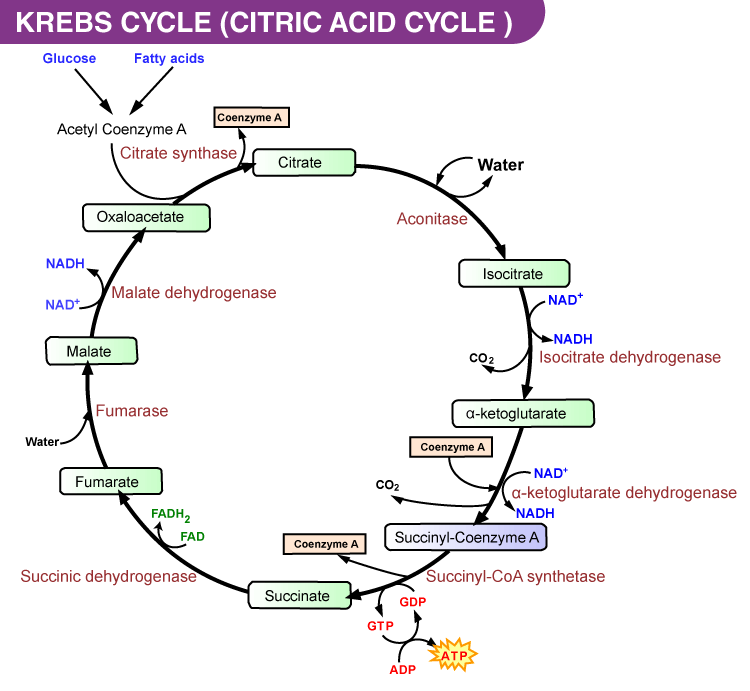
How Many Atp Are Produced In Glycolysis And Tca Cycle Byju S Neet

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy
What Are The Products Of Glycolysis Quora
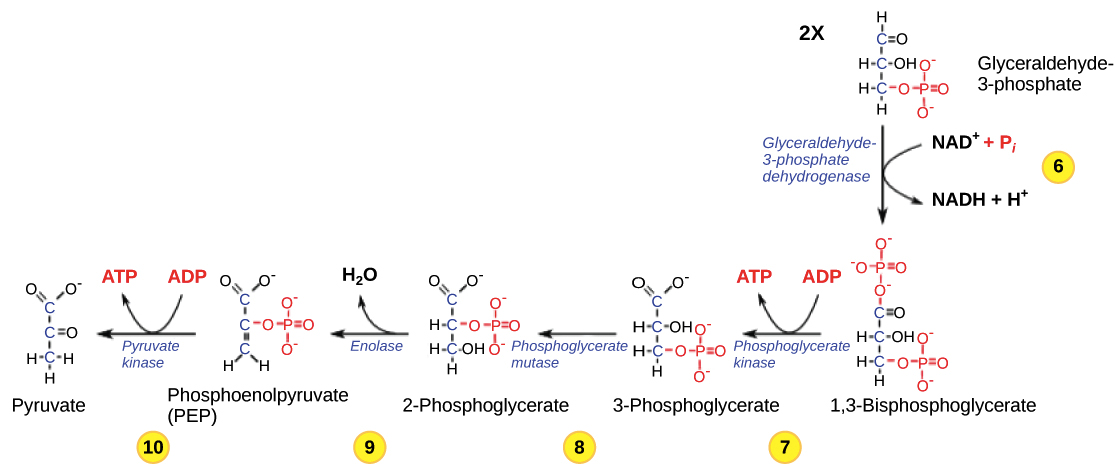
Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

Topic 8 2 Cell Respiration Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Generation Of Metabolic Energy Organic Molecules Cells Activity Metabolism

18 3a Glycolysis Biology Libretexts
How Did The Earliest Organisms On Earth Most Likely Produce Atp Lisbdnet Com

Cellular Atp Provision Defines The Rate Of Aerobic Glycolysis Download Scientific Diagram
How Many Atp Are Produced In Glycolysis And Tca Cycle Byju S Neet



Comments
Post a Comment